Differences in encryption
Using an encryption method, a plaintext is converted into a ciphertext (and vice versa). The decisive difference between the individual encryption methods is the point at which the data is encrypted, or rather who owns the key for encoding.
Basis: HTTPS/SSL encryption
HTTPS/SSL encryption secures the transmission path between the end device and the server. During the transmission through the Internet, the data remains encrypted. The data is transmitted along with the key to the respective service provider for storage. Before and afterward, the data is therefore decrypted, i.e. stored on the server with plain text.
Note: Providers often claim this to be "End-to-end encryption".
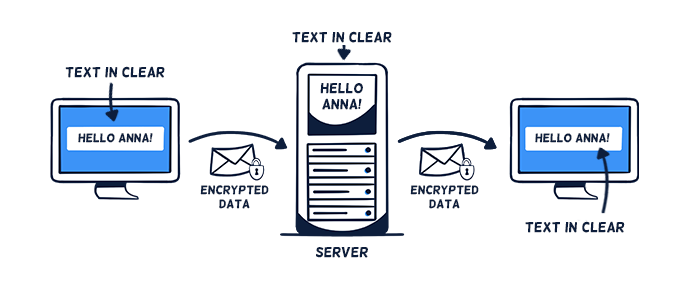
HTTP/SSL encryption only
Depending on the type of data, all data protection requirements under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) may be met by Stackfield (with its technical and organizational measures) even with HTTPS/SSL encryption only (i.e., for our rooms / Direct Messages without enabled end-to-end encryption).
Additionally: End-to-end encryption
In addition to the HTTPS/SSL encryption, Stackfield allows you to activate end-to-end encryption, which is a unique combination of symmetric (AES) and asymmetric (RSA) encryption methods.
During the upload, the data will be encrypted directly in the browser (i.e. a password is generated automatically) and then transmitted using HTTPS/SSL encryption. With client-side encryption, the key that encodes the data never leaves the user's possession. This means, that no one can decrypt the information between the two end devices. Only when downloading the data in the browser of the authorized recipient it will be decrypted, i.e. displayed as plain text.
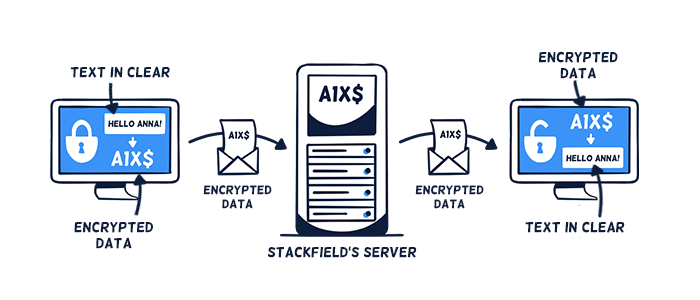
HTTP/SSL + end-to-end encryption
This data is end-to-end encrypted
(Dis-) Advantages of end-to-end encryption
If end-to-end encryption is enabled in Stackfield, no unauthorized third party has access to the information - neither the state / a court, nor Stackfield as platform operator or our subcontractors. If an outside party were to obtain the data, it would merely be a string of numbers and letters from which no information could be obtained. Only authorized individuals (i.e. members of a room with appropriate rights) can access the information.
Due to the early encryption, there may be some limitations in everyday work with end-to-end encrypted rooms / Direct Messages:
Good password management is essential, otherwise access cannot be restored in case of lost rooms / Direct Messages. Each user should therefore know their own login password at all times.
If two-factor authentication is enabled, the second factor also needs to be accessible.
Due to the encryption, no data is sent to the "outside", e.g. to external services such as a calendar subscription or notifications via email / on the lock screen of a cell phone. In email notifications, only general information about the existence of the item, including reference to the extra encryption, and link (i.e. a redirect to the relevant location in Stackfield) is disclosed.
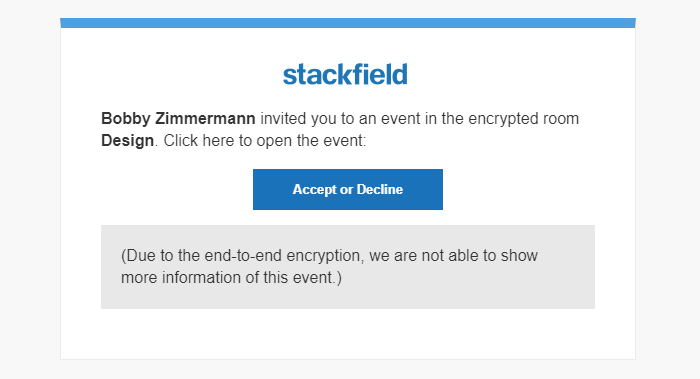
Example: Email notification from an end-to-end encrypted room
The global search may be a bit slower, since it does not run in one go due to the end-to-end encryption but in blocks. The speed depends on the local device and the amount of data.
In which cases is end-to-end encryption useful?
The top priority is to ensure compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), professional obligations (e.g. § 203 – German penal code), and compliance guidelines. We, therefore, recommend storing highly sensitive data (e.g. types of personal data and company internals) in our end-to-end encrypted rooms or private chats. Access here is restricted solely to the members of the room / chat with the appropriate rights.
Note: Further information on personal data and its processing can be found in particular in the Articles 4, 5, and 9 of the GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation
Want to learn more about end-to-end encryption?
How do I enable end-to-end encryption?
Arrangements made by the admin of the organization
Admins of the organization can make arrangements for the encryption in the "Organization Settings". The following functions can be defined here in more detail:
- Do you want to end-to-end encrypt Direct Messages? (Options: "Always disabled" / "Always enabled")
- Do you want to end-to-end encrypt all rooms? (Options: "Always disabled" / "Always enabled" / "Creator can choose"*)
- *Who is allowed to create rooms without enabled end-to-end encryption? (Triggered by the previous "Creator can choose" option) (Options: "Admins" / "Admins & Members")
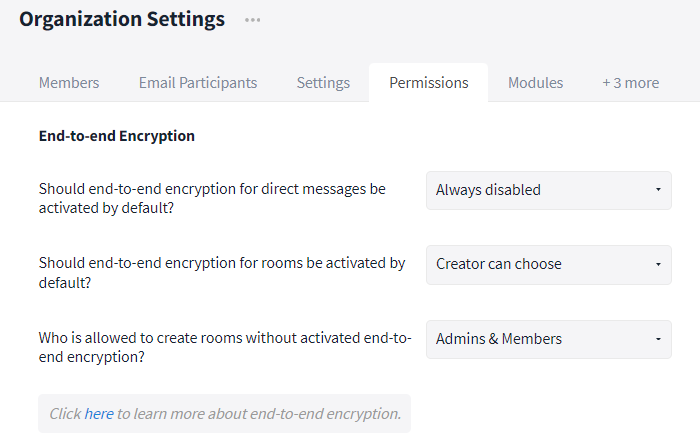
Encryption settings
After the activation we recommend communicating the advantages and disadvantages and especially the proper password management to all users (see: Password Management).
Creator can choose when creating a room
If the users themselves can decide on the additional end-to-end encryption when creating a room, a lock symbol is shown in the input field of the "Room name". With a click on it, the extra encryption can be activated. Note: The encryption of a room cannot be changed later.
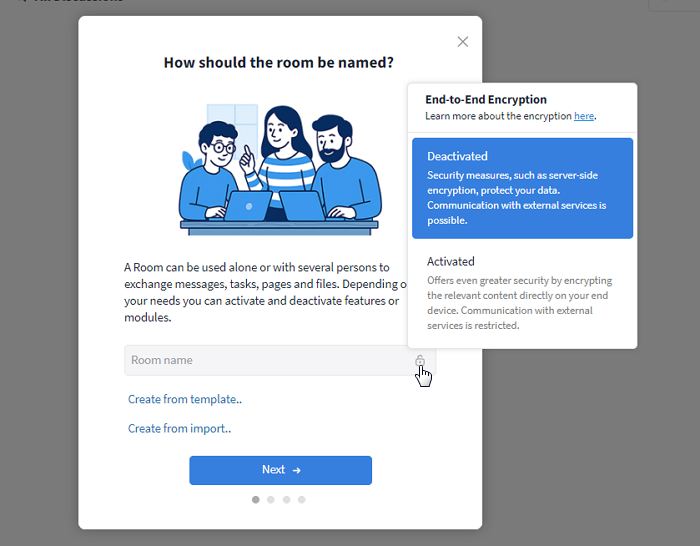
Activate / deactivate end-to-end encryption when creating a room
What do I need to do as an admin after enabling end-to-end encryption?
After enabling end-to-end encryption in the "Organization Settings", we recommend raising awareness of topics such as security, password management, and end-to-end encryption among all employees. Introduce mandatory (online) training and/or send out usage guidelines with links to relevant Learning Center articles:
In particular, address password management and the difference between login password and room / chat password. Make sure that for end-to-end encrypted rooms / chats, the room / chat password is secured by at least one admin. To avoid the responsible people (e.g. everyone / admins / a certain person) forgetting the password backup, anchor it additionally as a rule in your organization's internal guidelines. A task can remind you and the affected users of the compliance.
Further information
Security standards
For further information on our security standards please visit:
https://www.stackfield.com/security
How can I tell that a room is end-to-end encrypted?
End-to-end encrypted rooms are marked with a lock icon next to their room name when open and have an automatically generated password in the General tab of the "Room Settings".
Password Management
(Note: For an easier understanding, the correlations are greatly simplified here. The technical details can be found in our whitepaper.)
Each end-to-end encrypted room / group chat has its own password. The password is generated automatically and is not identical to your login password. To provide you with easy access to your end-to-end encrypted rooms / chats, your login password is automatically "linked" to all room / chat passwords in the background. This way, you usually do not need to enter your password manually when opening the room / chat.
Pay attention: When resetting your login password, the "link" to the room / chat passwords gets lost (since the old and new login passwords do not "meet") and must be restored first. To regain access, you have to enter the room / chat password manually or have it activated by an admin (see: Password reset).
If your password is merely changed, the link remains intact, as it is automatically transferred from your old login password to the new one. A manual input of the room or chat passwords is therefore not necessary.
Always make sure to store the password of end-to-end encrypted rooms / group chats / private chats in an additional (secure) place outside the encrypted environment. Especially for rooms / chats in which you are the only person or even the admin, you should write down the password. Since the passwords do not change, a one-time backup is sufficient.
The password of rooms / group chats can be found in the settings of the room / group chat. In the General tab, it is displayed in encrypted form until you click on the "Show" button - protected from unauthorized access.
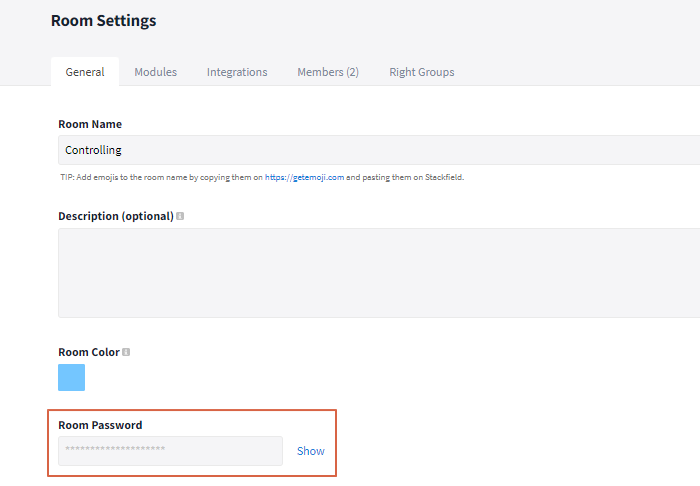
You can find the room password in the room settings
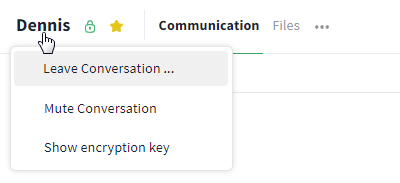
To view the password of a 1:1 chat, open the corresponding chat and click on the name of your communication partner in the upper left corner. Now, select the option "Show encryption key" to show the password.
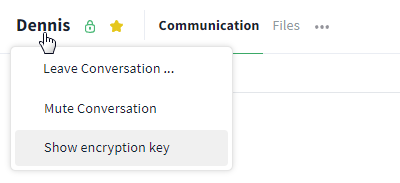
The password of a 1:1 chat is accessed via the name
Activate / Deactivate end-to-end encryption for chats retrospectively
End-to-end encryption settings only apply to private chats that are created after the (de-) activation. Old chats remain with / without end-to-end encryption. To adapt a private chat to the new setting, delete it and ask the other person to leave the chat as well. Note that deleting the chat will result in the loss of all chat content. Save important content separately if necessary.
Delete the chat
If the chat has been deleted by both communication partners, you can start the chat again.* Simply open it (e.g. via Global Search, Ctrl + k) and write a message. The new settings for end-to-end encryption have now been applied.
*If the chat is started before both people have exited, the settings will not be applied and the process will have to be restarted.
Optional data sharing for end-to-end encrypted rooms and its technical implementation
(Note: For an easier understanding, the correlations are greatly simplified here. The technical details can be found in our whitepaper.)
What happens when a file is called up / data is exported from end-to-end encrypted rooms?
What happens when content is sent via API / email forwarding in an end-to-end encrypted room?
The content received by Stackfield via the API or email integration is encrypted after transmission via SSL using a randomly generated key. This key is in turn stored in encrypted form using an algorithm that includes the room password and can then only be decrypted by authorized users. As soon as this process has been completed, the generated information is immediately deleted from the cache of the Stackfield infrastructure. Stackfield does not have access to the encryption key of the respective room at any time during this process.
If the transferred content is edited at a later point in time, the initial key is also exchanged with the room password, which further increases security.